Rubber Lining Procedure-Metal to Rubber Bonding Process
Detailed explanation of the rubber lining procedure for Lina-tex-type rubber materials, including the steps and technical key points of the metal-to-rubber bonding process.
- Metal Surface Preparation Process:
- Rubber Surface Preparation Process:
- Metal-Rubber Bonding Process:
Metal Surface Preparation Process:
Step 1. Grinding and Roughening:
Grind, grit blast, or roughen the metal surface to achieve a surface profile of 80 microns. After this, ensure the metal surface is thoroughly cleaned to remove any contaminants.

Step 2. Surface Pre-treatment:
Within 4 hours of blasting, apply a metal pre-treatment agent (e.g., LOCTITE SF-7467) to the cleaned and dried metal surface. This pre-treatment ensures better adhesion.

Step 3. Removal of Pre-treatment Agent:
After applying the pre-treatment agent for 1 minute (do not exceed 5 minutes), remove the excess using an absorbent foam roller and absorbent paper. This treatment can protect the metal surface from rust for up to 7 days.
Step 4. Applying LPT1205 Metal Adhesive:
Thoroughly mix the LPT1205 metal adhesive before application. Using a brush or roller, apply a uniform layer to the prepared metal surface. After application, allow the adhesive to dry naturally at room temperature for 60 minutes. If possible, applying heat will improve the bonding performance. The typical dry film thickness should be between 5.1–10.2 microns. After the adhesive is applied, ensure the metal parts are stored properly, protected from dust, oil, and moisture, and the maximum storage time should not exceed one month.

To learn more about the operation instructions and safety guidelines for LPT1205, please click to download: LPT1205 MSDS, LPT1205 TDS.
Alternative Products:
Customers can also use CHEMLOK 205 and CHEMLOK 220 products. First, apply a layer of CHEMLOK 205 to the treated metal surface. Once fully dried, apply a second layer of CHEMLOK 220.
Note:
If vulcanization is required, after the adhesive is applied, place the treated metal workpieces into the hot mold. Quickly fill with rubber and close the mold to prevent premature curing of the metal adhesive, which could lead to failure. Ensure that both the metal adhesive and rubber cure simultaneously. The curing time should align with the vulcanization time to achieve the best bonding performance.
Rubber Surface Preparation Process:
Step 1. Grinding:
Use a tungsten carbide grinding wheel to roughen the uncontaminated rubber bonding surface. During grinding, take care to avoid polishing or burning the rubber. After grinding, clean the rubber surface thoroughly. If the rubber has been pre-treated with single-sided roughening at the factory, no further treatment is necessary.

Step 2. Cleaning and Drying:
Clean the rubber surface with LPT360 Cleaning Agent to remove dirt and residues. After cleaning, allow the surface to dry naturally or apply heat to dry it completely, ensuring the rubber is free of moisture.
Step 3. Cutting the Rubber:
Mark and cut the rubber into the required shapes and sizes.
Joint Treatment:
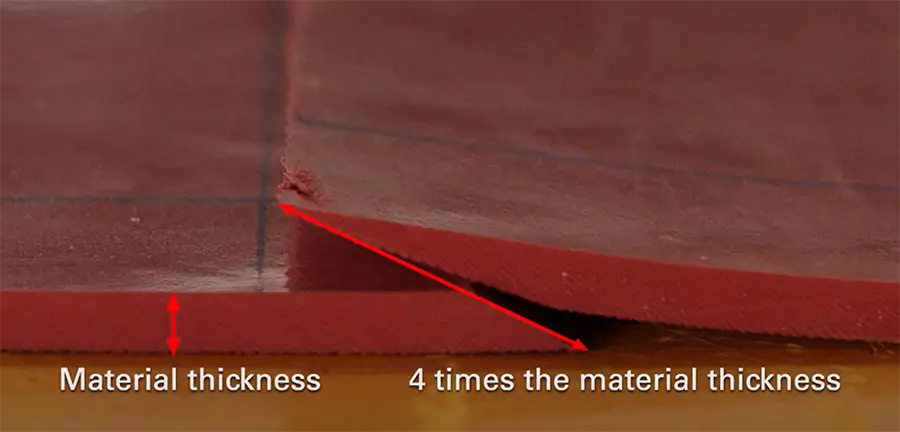
Typically, a standard trapezoidal lap joint is used, ensuring that the length of the sloped overlap at the joint is at least twice the thickness of the rubber.
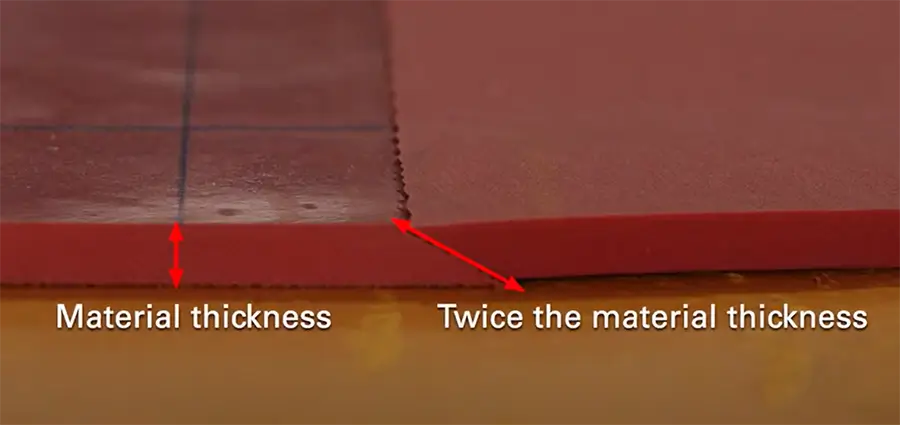
For applications where the environment is acidic or highly corrosive, such as water tank linings, use an overlapping trapezoidal joint, where the length of the sloped overlap should be four times the rubber thickness.

Step 4. Applying Rubber Treatment Agent:
Pour LPT366 Rubber Treatment Agent B component into the A component and mix thoroughly until B is completely dissolved. Note: The mixed treatment agent should be used within 4 hours.
After mixing, apply a uniform coat of the rubber treatment agent to the prepared bonding surface of the rubber. Allow it to dry naturally or accelerate the drying process with heat.
To learn more about the operation instructions and safety guidelines for LPT 366, please click to download: LPT 366 MSDS ,LPT 366 TDS .
Metal-Rubber Bonding Process:
Step 1. Mixing the Adhesive:
Mix LPT3008 Adhesive and ER65 Curing Agent in a 100:5 weight ratio. Ensure the mixture is thoroughly blended.
Note: The mixed adhesive must be used within 3 hours. Each 3.5 kg drum of LPT3008 Adhesive covers approximately 4 square meters of rubber.
Step 2. Applying Adhesive to Rubber and Metal Surfaces:
Apply the adhesive in two coats, ensuring each coat is evenly spread to ensure full penetration of the adhesive into the bonding surface. After the first coat, allow it to dry completely before applying the second coat. This can be done in one day or over two days.

To learn more about the operation instructions and safety guidelines for LPT 3008, please click to download: LPT 3008 MSDS, LPT 3008 TDS, ER 65 MSDS.
Step 3. Bonding:
Once the second coat is dry to the touch and no longer sticky, begin the bonding process. Align the two bonding surfaces and press them together. Use a rubber hammer to tap from the center outward, ensuring the surfaces are tightly bonded and any air pockets are removed.
Step 4. Post-Bonding:

After completing the bonding, wait at least 3 hours before proceeding with any cutting or grinding operations on the rubber. Allow the bonded materials to rest for a minimum of 24 hours to ensure sufficient bonding strength.